Gastric cancer is one of the malignant tumors that seriously endangers human life. The survival rate of gastric cancer patients is closely related to the progression of gastric cancer. The cure rate of early gastric cancer can reach 90%, or even be completely cured. The cure rate of mid-stage gastric cancer is between 60% and 70%, while the cure rate of late-stage gastric cancer is only 30%. So detecting early gastric cancer and treating it early is the key to reducing gastric cancer mortality. Fortunately, in recent years, with the improvement of endoscopic technology, early gastric cancer screening has been widely carried out in my country, which has greatly improved the detection rate of early gastric cancer; So, what is early gastric cancer? How to detect early gastric cancer? How to treat it? 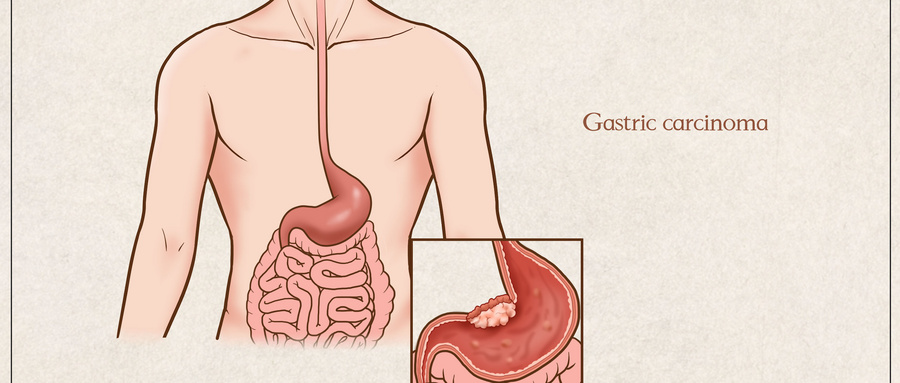
1. The concept of early gastric cancer
Clinically, early gastric cancer mainly refers to gastric cancer with relatively early lesions, relatively localized lesions, and no obvious symptoms. Early gastric cancer is mainly diagnosed by gastroscopy biopsy pathology. Pathologically, early gastric cancer means that the cancer cells are limited to the mucosa and submucosal layer. Regardless of the size of the cancer and whether there is lymph node metastasis, it is classified as early gastric cancer. In recent years, severe dysplasia and high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia have also been classified as early gastric cancer. Early gastric cancer is divided into small gastric cancer according to the size of the tumor: the diameter of the tumor is 6 to 10 mm. Microgastric cancer: The diameter of the tumor is ≤5 mm. Punctate carcinoma: gastric mucosal biopsy shows cancer, but no cancerous tissue can be found in a series of surgical resection specimens. Endoscopically, early gastric cancer is further divided into: Type (polypoid type): The cancer mass protrudes by more than 5 mm. Type (superficial type): The bulge or depression of the cancer is within 5 mm. Type (ulcer type): The depth of the cancer mass is more than 5 mm, but does not exceed the submucosal layer.
2. What are the symptoms of early gastric cancer?
Most early gastric cancers have no special symptoms. That is to say, the early symptoms of gastric cancer are that there are no symptoms. The so-called early signs of gastric cancer circulated on the Internet are not actually early signs. It is difficult for both doctors and patients to judge based on symptoms and signs. Some people may have some non-specific symptoms, mainly indigestion, such as abdominal pain, bloating, early satiety, loss of appetite, acid reflux, heartburn, belching, burping, etc. These symptoms are very similar to common stomach problems, so people often don’t take them seriously. Therefore, for people over 40 years old, if they have obvious symptoms of indigestion, they should go to the hospital in time and undergo a gastroscopy if necessary, so as not to miss the best opportunity to detect early gastric cancer.
3. How to detect early gastric cancer
Early gastric cancer screening is mainly targeted at some high-risk patients, such as patients with Helicobacter pylori infection, patients with a family history of gastric cancer, patients over 35 years old, long-term smokers, and those who like to eat pickled foods. The primary screening method is mainly through serological examination, that is, through gastric function and Helicobacter pylori antibody detection, to identify high-risk groups for gastric cancer. Then, the high-risk groups discovered during the initial screening process will be carefully examined through gastroscopy, and methods such as magnification, staining, and biopsy will be used to observe the lesions in more detail, so as to determine whether the lesions are cancerous and whether they can be treated under the microscope. Of course, incorporating gastroenteroscopy into routine physical examinations through physical examinations in healthy people is also a better way to detect early gastric cancer.

4. What is the gastric function test and gastric cancer screening scoring system?
The gastric function test is to detect the levels of pepsinogen I (PGI), pepsinogen II (PGII), protease gen ratio (PGR, PGI/PGII), and gastrin 17 (G-17) in the serum. Gastric cancer screening The scoring system is a method of judging the risk of gastric cancer based on the results of gastric function tests, combined with comprehensive scores such as Helicobacter pylori antibodies, age and gender. Through the gastric cancer screening scoring system, people at medium and high risk of gastric cancer can be screened. Intermediate and high-risk groups will undergo intensive endoscopy and follow-up. High-risk groups will undergo gastroscopy at least once a year, and medium-risk groups will undergo gastroscopy at least every 2 years. If the cancer is actually found early, endoscopic surgery can be performed. This can not only improve the early detection rate of gastric cancer, but also reduce unnecessary endoscopies for low-risk groups.
5. What is gastroscopy?
Simply put, precise gastroscopy is to conduct endoscopic morphological analysis of suspicious lesions found during routine gastroscopy, including ordinary white light endoscopy, chromoendoscopy, magnifying endoscopy, confocal endoscopy and other methods. The lesion is determined to be benign or suspected malignant, and then the suspected malignant lesion is biopsied, and the final diagnosis is confirmed through pathology. This way we can determine whether it is a cancerous lesion, the lateral invasion range of the cancer, the depth of vertical invasion, the degree of differentiation, and whether there are any indications for microscopic treatment. Compared with ordinary gastroscopy, precise gastroscopy must be performed under painless conditions, allowing patients to completely relax themselves during a short sleep state and perform gastroscopy safely. Precision gastroscopy has high requirements on personnel. It must be trained in early cancer diagnosis and experienced endoscopists can conduct more detailed examinations, so that they can better detect lesions and make reasonable examinations and judgments. Precision gastroscopy has high requirements on equipment, especially gastroscopy equipment with image enhancement technologies such as chromoendoscopy /electronic chromoendoscopy or magnifying endoscopy. Ultrasound gastroscopy is also required when necessary.
6. Treatment methods for early gastric cancer
1. Endoscopic resection Once early gastric cancer is diagnosed, endoscopic resection is the first choice. Compared with traditional surgery, endoscopic treatment has the advantages of less trauma, fewer complications, faster recovery, and lower cost, and the efficacy of the two is basically the same. Therefore, endoscopic resection is recommended at home and abroad as the preferred treatment for early gastric cancer. Currently, the commonly used endoscopic resections mainly include endoscopic mucosal resection ( EMR) and endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD). ESD was developed from EMR and is a new technology developed to avoid the limitations of EMR in terms of tumor infiltration and area size. The single-channel endoscope of ESD can achieve one-time en bloc resection of lesions deep into the muscularis propria, while also providing accurate pathological staging to minimize late recurrence. It should be noted that endoscopic resection is a minimally invasive surgery, but due to factors such as equipment, operator experience, technical methods, and patient's general condition, there is still a high incidence of complications, including bleeding, perforation, Stenosis, abdominal pain, infection, etc. Therefore, patients must actively cooperate with doctors in post-operative care, recuperation, and review in order to recover as quickly as possible. 
2. Laparoscopic surgery Laparoscopic surgery may be considered for patients with early-stage gastric cancer who cannot undergo endoscopic resection. Laparoscopic surgery is to open tiny channels in the patient's abdomen. The laparoscope and operating instruments are inserted through these channels that cause little harm to the patient. The image data in the abdominal cavity is transmitted to the display screen through the laparoscope, and is completed under the guidance of the laparoscope. Gastric cancer surgery. Laparoscopic surgery can complete the operations of traditional laparotomy, including subtotal or total gastrectomy, removal of suspicious lymph nodes, etc., with less bleeding, less damage, small postoperative incision scars, less pain, and quick recovery of gastrointestinal function after surgery. 
3. Laparotomy Since 5% to 6% of intramucosal gastric cancer and 15% to 20% of submucosal gastric cancer have perigastric lymph node metastasis, especially undifferentiated adenocarcinoma in young women, traditional laparotomy can be considered, which can radically remove and Lymph node dissection.

Although gastric cancer is very harmful, it is not terrible. As long as the prevention awareness is raised, gastric cancer can be detected in time in the early stages and treated early, and it is possible to achieve complete cure. Therefore, it is recommended that high-risk groups after the age of 40, regardless of whether they have digestive tract discomfort or not, should undergo early screening for gastric cancer, or a gastrointestinal endoscopy must be included in the normal physical examination. If a case of early cancer is found, a life can be saved and a happy life can be achieved. family. |






